Definition
What is a ROADM?
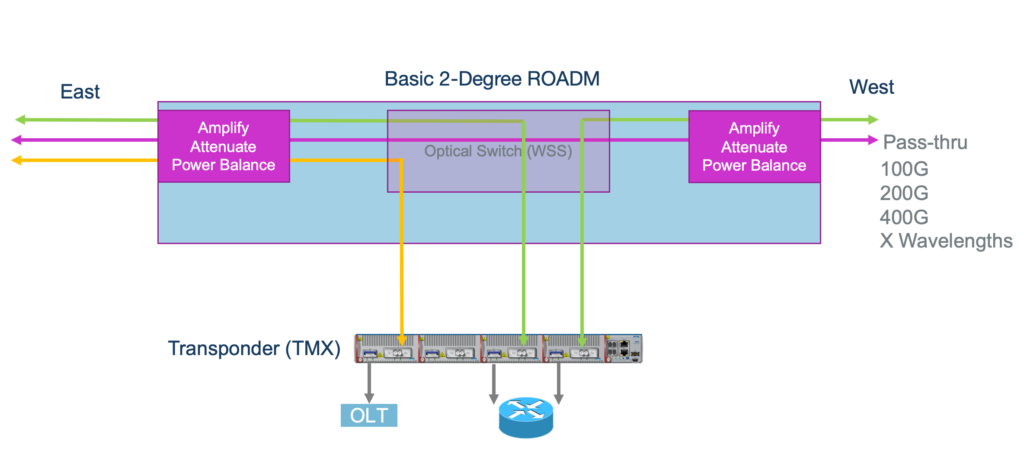
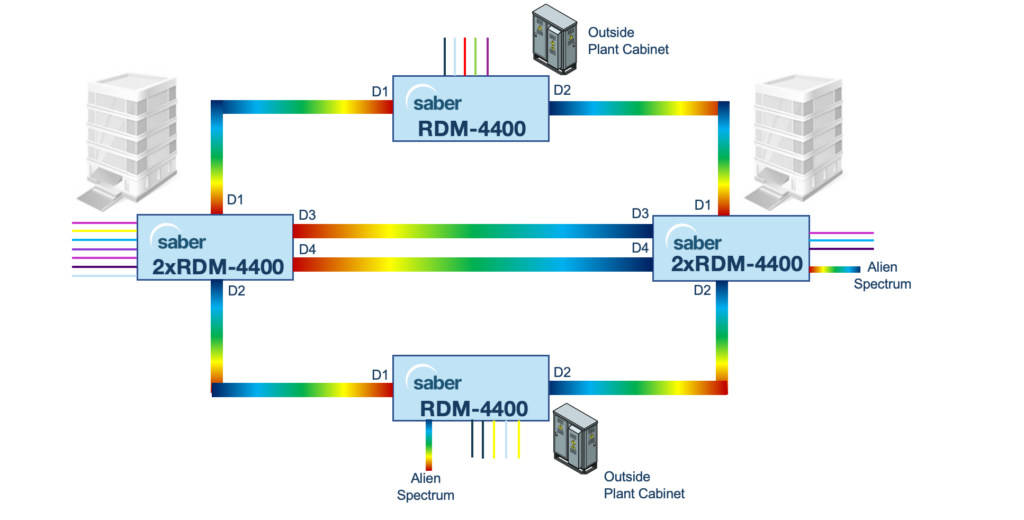
ROADMs improve DWDM transport network flexibility, effectiveness, and scalability by enabling the dynamic management and reconfiguration of optical wavelengths in a transport network. Reconfigurable Optical Add-Drop Multiplexers (ROADMs) consist of several essential components and come as colorless, directionless and contention less (CDC) options with flexible grid or all these attributes combined:
- Multiplexer/demultiplexer: These components combine and separate multiple optical wavelengths on a single fiber. Multiple data channels can transmit over a single optical fiber through this.
- Add-drop ports: ROADMs feature add and drop ports, which allow network operators to add or remove specific wavelengths or data channels from the signal without affecting the rest of the traffic. This flexibility is important for network reconfiguration.
- Switching matrix: The core of a ROADM is its switching matrix, which enables the dynamic rerouting of optical signals. Operators can, remotely and in real-time, select the appropriate input and output ports for each wavelength.
Contact us to learn more optical transport and ROADM technology and solutions.
Related Resources
Products:
Solutions & Initiatives:
White Papers:

